CMMS downtime software gives the maintenance manager a way to identify trouble equipment quickly. By identifying these issues quickly and accurately equipment uptime is maximized. This post instructs on how to use the downtime software module in MaintSmart. Other benefits to using CMMS downtime software are listed below:
- Reduce equipment downtime.
- Reduce product losses associated with process interruptions.
- Optimize maintenance scheduling.
- Prioritize and optimize preventive maintenance based upon MTBF.
- Reduce spares usage.
- Extend the overall life of the equipment.
- Reduce emergency repairs (corrective maintenance) so technicians can focus on preventive maintenance.
Entering CMMS Downtime Software Data
For the purposes of this post downtime refers to unexpected breakdown of equipment. This also includes a stoppage or other interruption of the process. Entering downtime records requires that some equipment and some failure cause definitions have been entered into the system. Downtime data should not be confused with repair or corrective maintenance work orders. Downtime is an instance of equipment failure whereas corrective work orders are an instance of work performed to correct the breakdown. Downtime is tacked separately so that it may be analyzed by itself. This gives the maintenance manager an accurate picture of equipment performance unpolluted by unrelated data.
Linking Downtime to a Corrective Work Order
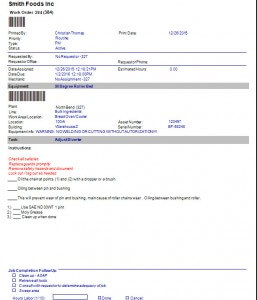
Since downtime is tracked and entered separately from work orders there needs to be a simple way to assign a corrective work order to manage this downtime instance. Fortunately there is. The CMMS has a downtime cause to remedial task mapping component. When a downtime record is entered simply check the check box labeled: Auto-Create Work Order Record. When the work order is saved a new work order is either automatically created or the user is prompted to select the corrective task from the dialog screen that appears. The selected task is then automatically mapped to this equipment and the failure cause. If this same breakdown cause reoccurs the task is automatically used next time. This saves time and provides consistency.
Configuring Downtime Causes
All data is configurable in MaintSmart. Downtime causes are used to describe the basic cause for an equipment failure. Downtime causes are grouped into Cause Groups for fast filtering during the selection of the exact cause during downtime CMMS record submission. Typical downtime cause groups are:
- Mechanical.
- Electrical.
- Sanitation Causes.
- <equipment name> Causes.
When naming cause groups and causes always begin with the most generic cause groups/causes and gradually move towards more specific groups/causes. This is explained in detail below.
Downtime and Work Orders
Typically a work order is one primary task with detailed instructions, SOPs, file attachments and parts linked to it. Downtime is an instance of equipment breakdown. A work order may be generated automatically from the CMMS downtime software module.
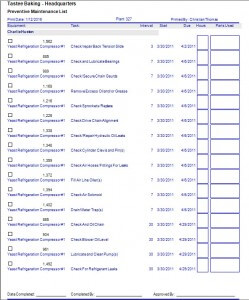
Downtime and Preventative Maintenance
Downtime data is used by the CMMS to suggest preventive maintenance task intervals. This accomplished through the use of MTBF derived from live downtime data after analysis by the reliability analysis module.
Downtime Causes and Cause Groups
Downtime causes are defined by the CMMS software user to fit the specific maintenance management operation. Causes are user-friendly brief explanations of the cause of the equipment failure. Below are a few examples of downtime causes that could be defined:
- Broken Wire.
- Operator Error.
- Water in Electrical.
There are no limits to how many failure cause definitions may be defined. Each cause definition may be up to 255 characters in length. Downtime may be analyzed by the cause. This is a very powerful feature for identifying trends and solving specific problems.
Linking a Work Order to Downtime
Downtime and Reliability Analysis
Other Downtime Analysis Capability
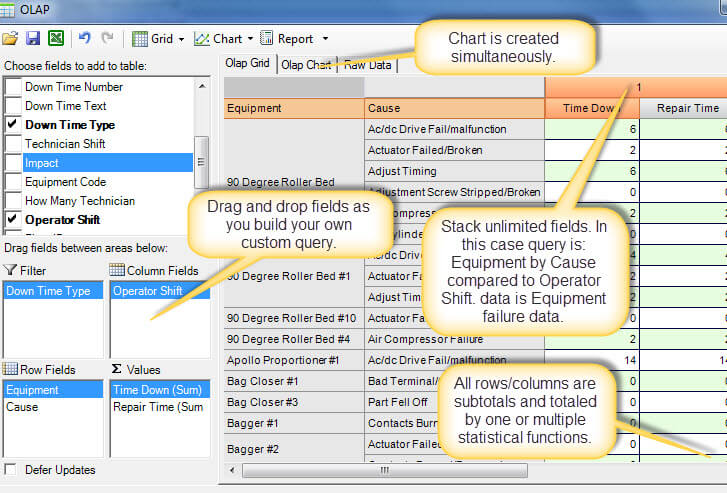
The downtime analysis module is flexible and powerful using several analysis techniques.
- Use the query builder to analyze any possible downtime scenario with drag and drop.
- Overall equipment effectiveness provides multiple CMMS KPIs using downtime data.
- Reliability analysis uses downtime data and compares MTBF with preventive maintenance task intervals and suggests optimized schedules.
- Extensive charting provides a visual depiction of downtime history.
- All downtime analysis data may be imported into Excel for further analysis with almost no effort.

Thanks for sharing this. CMMS software can do an incredible amount to minimize the amount of downtime when there’s an issue with a particular machine or system. Knowing when a machine is about to go down allows management to schedule maintenance in time to address the problem quickly and get the machine running again, which goes a long way to reducing the amount of revenue lost due to maintenance.
A great article on the CMMS Downtime Tracking Software and its advantages for having high uptime. The author has brought to light the main insights the software gives to the managers through which a higher uptime can be managed and productivity can be given the much needed boost.
A great article on the CMMS Downtime Tracking Software and its advantages for having high uptime. The author has brought to light the main insights the software gives to the managers through which a higher uptime can be managed and productivity can be given the much needed boost.
[…] equipment downtime and reliability. What is the MTBF (average time between equipment failures) for various […]